
What Is A Chocolate Cyst?
February 4, 2023
What Is Adenomyosis?
February 23, 2023
What Is A Chocolate Cyst?
February 4, 2023
What Is Adenomyosis?
February 23, 2023
What Is An Ectopic Pregnancy?
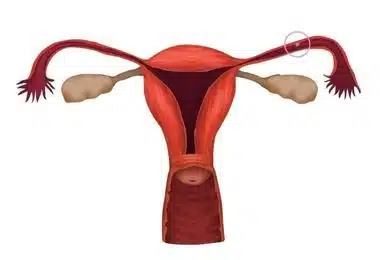
Image-1: Ectopic pregnancy.
It is also known that high levels of the hormone progesterone increase the chance of ectopic pregnancy by slowing down passage through the fallopian tubes. Problems with a fertilized egg can also increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. In addition to the tubes, an ectopic pregnancy can be located in the ovaries, the cervix outside the endometrial cavity of the uterus or the angular sites of the connection of the tubes with the uterus, and also, less often, in the cervix. old cesarean section incision (scar pregnancy). Very rarely, pregnancy can occur both inside the uterus (intrauterine) and outside the uterus (ectopic) at the same time, and the incidence of this condition has been reported to be one in 60,000 in natural pregnancies and one in eight thousand in pregnancies with assisted reproductive technologies such as like in vitro fertilization.
What Is the Frequency of Ectopic Pregnancy?
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy among pregnant women worldwide is reported to be approximately 1 to 2 percent. Most of them occur in the tubes (fallopian tubes). The remaining settlements make up less than 10 percent. In addition to the tube, the places where an ectopic pregnancy is located are called the cervix (cervix), the corner of the uterus (cornu), a cesarean section (scar pregnancy), the ovary, or the inside of the abdomen, and these areas are relatively rare places where an ectopic pregnancy occurs. . The spleen, near the liver, and the peritoneal area covering the abdomen are other reported sites of ectopic pregnancy. Those with a previous ectopic pregnancy, older pregnancy, pregnancy with assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization, pregnancy with those with a previous ectopic pregnancy, and pregnancies in women with previous surgery or infection represent a more high risk of ectopic pregnancy.
How Is Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
The symptoms of ectopic pregnancy at first are the same as those of a normal, healthy pregnancy. In other words, nausea, morning sickness, loss of appetite, mood changes, and missed periods are similar in both normal intrauterine and ectopic pregnancies. When delayed women take a home pregnancy test or find beta-hCG in their blood, the result is pregnancy+. Bleeding and pain in the groin that occurs after a missed period in an ectopic pregnancy are considered typical manifestations of the triad. When the level of the hormone beta-hCG in the blood is 1500 IU/ml, it is expected that the gestational sac in the uterus can be seen with a vaginal ultrasound in a singleton pregnancy. If the level of beta-hCG in the blood is above 1500 IU / ml, but no gestational sac is visible in the uterus, an ectopic pregnancy is suspected.
From this, we can conclude that all women with delayed menstruation should be examined by a gynecologist and obstetrician to understand whether they are pregnant or not. With a gynecological examination and beta-hCG, you can understand whether intrauterine or ectopic pregnancy, twins, or triplets. In addition, with such an examination, it will be easy to understand whether there are problems such as uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts.
What Conditions Can Be Associated with Ectopic Pregnancy?
There are both medical and surgical treatments for ectopic pregnancy. While methotrexate, which prevents cell division, is used as a medical treatment, both open and laparoscopic (closed) surgical methods can be used as a surgical treatment. Again, among the surgical options, there are surgical options that can be considered radical, such as removing the tube that contains the ectopic pregnancy (salpingectomy), while there are more conservative surgical options, such as opening the tube and removing only the material of the pregnancy. and leaving the tube (salpingostomy). Medical treatment with methotrexate is used in relatively small cases of ectopic pregnancy and has a satisfactory chance of success.
If a weekly decrease in beta-hCG levels can be achieved after administration of the drug, it is monitored, and if a plateau or increase in beta-hCG levels occurs, additional treatments are considered. Surgical treatment is used in cases where the treatment time has expired, and in cases where medical treatment has not helped. While patients without bleeding or with very little bleeding, i.e. hemodynamically stable patients, can be treated with laparoscopic (closed) surgery, open surgery is preferred in patients who need to be operated on as quickly as possible without wasting time preparing for laparoscopy.
In essence, the choice of medical treatment or surgery, and if surgery is to be used, whether open or closed (laparoscopic) surgery, is decided solely on the basis of the patient's condition.
While deaths due to ectopic pregnancies have been observed in previous periods, today ectopic pregnancies can be diagnosed very early thanks to the observation of both beta-hCG and advanced ultrasound equipment. Thanks to early diagnosis, this disease has ceased to be fatal disease, at least in the modern world.
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Reoccur?
Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy before having an increased risk of having an ectopic pregnancy in their next pregnancy compared to the normal population. While one reason for this increased risk is the underlying antecedent factors, another reason seems to be the treatments applied for ectopic pregnancy. For all these reasons, it is vital for women who have had an ectopic pregnancy to be examined by gynecology and obstetrician in their later pregnancies and to determine what kind of pregnancy the pregnancy is.

