
High-Risk Pregnancy
November 15, 2022
Blood Incompatibility
November 15, 2022
High-Risk Pregnancy
November 15, 2022
Blood Incompatibility
November 15, 2022
What Its Amniotic Band Syndrome?
Amniotic band syndrome is a malformation of the inner layer of the placenta, called the amnion resulting in the formation of thin strands of tissue that stick to the fetus and wrap some parts of its body (arms, legs, or umbilical cord). According to available data, the probability of this ranges from about 1 case per 2000 and 15,000 births.

Image-1: Baby born with Amniotic Band Syndrome.
The amniotic membrane, which contains the amniotic fluid, normally adheres to a structure called the chorionic membrane after the first trimester of pregnancy. It allows the fetus to move freely and contributes to the preservation of amniotic fluid. However, in some cases, for reasons unknown to medicine, the amniotic membrane sticks to the fetus's body, tangling around some of its parts. This condition is called amniotic band syndrome. There are two theories that try to analyze the formation of amniotic bands. The most popular of them explains it by a partial rupture of the amniotic sac in the early stages of pregnancy.
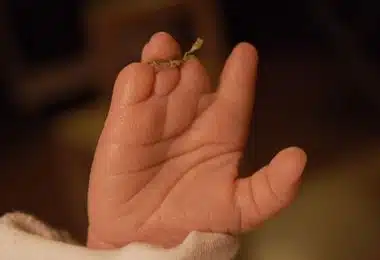
Image-2: Baby born with Amniotic Band Syndrome.
It is the fibrous filaments that arise from the rupture that tangle around the developing fetus. With the growth of the fetus, bands, squeezing the place where it is located, begin to restrict blood flow. For example, the formation of bands on the arm causes the lack of blood supply, and, as a result, abnormalities in the development of the limb, and in the most severe case, amputation. If it forms on the umbilical cord, the fetus can die from a lack of oxygen and nutrients. This theory forms the scientific basis for explaining fetal abnormalities. Another theory explains the formation of amniotic bands by abnormalities in one of the stages of fetal development, called the "embryonic disk". According to it, vascular damage that occurs during the development of the embryonic disc causes a violation of blood circulation in the area and, as a result, necrosis (tissue death). This theory also provides a scientific basis for explaining anomalies and raises the question of the rationality of fetoscopic treatment in cases of amniotic band syndrome.
What Baby Health Issues Does Amniotic Band Syndrome Cause?
Baby health issues that amniotic bands can cause depend on which part of the body they are in contact with. The main threat of bands is that they can restrict blood flow to the lower part of the baby's body, so the area to which they are attached determines the fate of the development of the disease. For example, bands formed on the arm or leg first cause restrictions of blood flow and then swelling since bands do not increase in size, and with the growth of the fetus, they squeeze the limbs. Aggravation of the situation first causes deformity, fractures, or bends of the affected part of the body, then underdevelopment and amputation. The formation of bands on vital parts of the body, such as the neck or umbilical cord, can cause the death of the fetus in the womb. The formation of amniotic bands on fingers or toes leads to deformation or even amputation.
How Is Amniotic Band Syndrome Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of amniotic band syndrome is usually made during ultrasound. Depending on the location, it causes swelling, deformity, or at an advanced stage, loss (amputation) of limbs. If color Doppler ultrasound is used to analyze blood flow, changes or even complete cessation of blood flow can be noticed. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as well as four-dimensional ultrasound, can provide additional information about the severity of each specific case.
How Is Amniotic Band Syndrome Treated?
As mentioned above, depending on the location of the formation, amniotic band syndrome can cause serious developmental abnormalities, defects, or even amputation of limbs. Therefore, it is vital to carry out intrauterine treatment before the appearance of complications. Removal (dissection) of amniotic bands is performed using a camera (fetoscope), which is inserted into the mother's womb. Fetoscope is a system with a diameter of about 3 mm inside which there is a 1-millimeter laser fiber channel, as well as another 1-millimeter instrument (dissector or scissors). This procedure usually requires regional anesthesia (spinal anesthesia) of the mother. The fetus is also given anesthesia through the umbilical cord and muscle relaxants (drugs that reduce muscle tone and decrease motor activity). During fetoscopy procedures of amniotic band removal, laser or dissector are usually used. To facilitate the treatment method choice, a classification of amniotic band syndrome was developed (Table 1). The determining factor in the planning of treatment is most often the fact of the presence of circulatory disorders in the affected limbs.
What Is the Success Rate of Intrauterine Treatment of Amniotic Band Syndrome, and What Are Its Risks?
It is reported that the life expectancy rate of babies who have undergone intrauterine amniotic band syndrome removal surgeries is approximately 90% to 100%. The success of surgeries depends on the team of surgeons, the instruments used, as well as the severity of the disease. Despite the high percentage of successful operations, the probability of maintaining the normal functioning of the affected limbs is approximately 67 to 100 percent. In cases when the irreversible damage to the fetus’s health is done, about 1/3 of women in labor experience premature water break, and about 2/3 of women in labor have premature births (before 37 weeks). All these points should be considered when planning the amniotic band syndrome treatment.
In conclusion, amniotic band syndrome is a malformation of the inner layer of the placenta, called the amnion resulting in the formation of thin strands of tissue that stick to the fetus and wrap some parts of its body (arms, legs, or umbilical cord), causing restriction of blood flow and, as a result, serious injuries to limbs or even death of the fetus. Fetoscopy methods are proven to be effective in the treatment of this disease. In the planning of treatment, the personal approach to each specific case is vital. Both in serious cases that require surgical intervention and in cases that do not threaten the health of the fetus, monitoring of the condition and performing operations should take place in well-equipped clinics with an experienced team of specialists who are ready to provide all the necessary help.
Sources
Fetoscopic Release of Amniotic Band Syndrome An Update Minella C et al J Ultrasound Med 2020.
Perinatal outcome after fetoscopic release of amniotic bands: a single-center experience and review of the literature Javadian P et al Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2013.

