Polyp Surgery
May 28, 2023
Use of Medicines and their Effects During Pregnancy
September 14, 2023
Polyp Surgery
May 28, 2023
Use of Medicines and their Effects During Pregnancy
September 14, 2023
What Is Fetoscopy?
How Is Fetoscopy Surgery Performed?
There are two methods of performing the fetoscopy procedure. One of them is to perform the procedure by opening the mother's womb and directly seeing the uterine wall, by entering through the uterine wall.
The second is performed by directly entering the skin on the anterior abdominal wall of the mother without opening the mother's womb. In both cases, anesthesia is applied so that the mother does not feel pain. This is usually in the form of regional anesthesia. Before the procedure, muscle relaxant drugs are given intramuscularly or inside the umbilical cord, depending on the gestational week and condition of the baby, so that the baby does not feel pain in the mother's womb and does not move with the anesthetic drugs, and the baby is immobilized by both anesthesia and muscle relaxation.
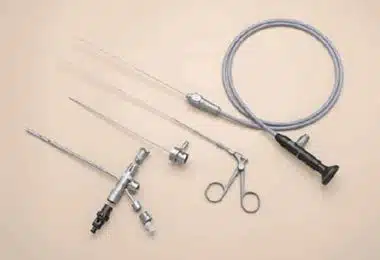
Figure 1: Fetoscopy tools.
After anesthesia is provided for the mother, the sheath of the fetoscopy apparatus is sent to the amniotic cavity where the fetus is located, and the fetoscopy procedure is started under the guidance of ultrasonography. The camera is generally 1 mm thick and fetoscopy is performed by passing it through a 3 mm sheath. There is another 1 mm wide channel inside the sheath so that the laser fiber can pass, or another tool can be sent to be used in case of need. By providing vision with the fetoscopy camera, the operations are performed by using the appropriate tools or equipment for the operation to be performed.
In Which Cases Is Fetoscopy Surgery Performed?
Fetoscopy is performed in a few cases for the treatment of unborn babies. These conditions include twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome in twin pregnancies, fetal cystoscopic laser valve ablation in posterior urethral valve cases, amniotic band syndrome, congenital diaphragmatic hernia (tear in the baby's diaphragm, that is, in the membrane separating the abdominal cavity and the thoracic cavity), fetal balloon placement in the trachea (fetal endotracheal balloon occlusion), fetal spina bifida (opening in the back of the babies and the membranes and nerve tissues coming out from there) are some of the areas where fetoscopy is used. In twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome, it has been scientifically proven that the treatment applied by removing the abnormal vascular connections that transfer the blood of one baby to the other by using laser with fetoscopy is superior to other treatments. Today, it is applied as the first choice in cases of twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome. Another situation where the benefit of fetoscopy is shown is the group of diseases called fetal lower urinary tract obstructions. What is meant by fetal lower urinary tract obstructions is the obstruction in the lower urinary tract of the baby in the womb and the inability of the baby's urine to come out of the urinary bladder easily. Posterior Urethral Valve is one of the most common of these obstructive problems. Posterior Urethral Valve (PUV) is explained as a separate topic on our website.
Fetoscopy in PUV cases not only allows differential diagnosis in cases such as urethral atresia (absence) and urethral stenosis (stenosis), which may be the cause of obstruction, and allows passage by destroying the valve in the Posterior Urethra, which causes problems in urine output, by using laser during fetoscopy. With fetoscopy, it is possible to intervene in cases of amniotic band syndrome, which affects the baby's extremities such as the umbilical cord or limbs, which causes the death of the baby in the womb, or development problems in the arms and legs, and even the absence of organs (amputation). Although the opening of the bands by fetoscopy in amniotic band syndrome cases varies according to the region affected by the band, it may contribute to the survival of the babies or the protection of extremities such as arms and legs.
Another situation in which fetoscopy can potentially be beneficial is a tear in the diaphragm called a congenital diaphragmatic hernia, and the intra-abdominal organs passing through the thoracic cage through this tear, negatively affecting the baby's lung development. In this case, there are positive data regarding that interventions performed by placing a balloon in the trachea with fetoscopy in some severe cases may contribute to the survival of infants.
Are There Risks (Complications) of Fetoscopy?
Fetoscopy is an operation that can affect both the mother and the baby in the final analysis. As with any surgery, it has some problems. Although rare, there is a possibility that anesthesia complications may occur due to the anesthesia applied to the mother. Regardless of the purpose of the fetoscopy procedure, the possibility of premature birth, early delivery of the baby's waters, failure of the procedure or loss of the baby is also possible, although rare, that varies from procedure to procedure and possible failure of the procedure.
Depending on the reason for the fetoscopy, specific problems may also occur, although rarely. For example, problems such as necrosis or fistulas created by laser in the tissues around the urethra in the posterior urethral valve case, or special conditions that may occur after fetoscopic intervention in twin-to-twin transfusion cases are complications that may occur with fetoscopy.
As a result, fetoscopy is an operation that can contribute to the elimination of some problems while babies are in the womb before they are born, thus contributing to the survival of babies or reducing their disability, thanks to the developments in today's technology.
Although there is a potential for treatment options for a limited number of diseases at the moment, it is thought that it will contribute to the treatment of more diseases with more success and less risk in the coming periods.
You can find the video of our case who was treated with fetoscopy for posterior urethral valve (fetal cystoscopic laser valve ablation) here.
You can find the video of our case who underwent fetoscopic amniotic band excision due to amniotic band syndrome here.

