
What Is Bartholin’s Gland Cyst?
November 15, 2022
Urinary Incontinence
November 15, 2022
What Is Bartholin’s Gland Cyst?
November 15, 2022
Urinary Incontinence
November 15, 2022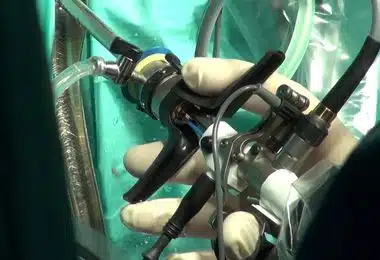
What Is Hysteroscopy?
Contents
- What Is Hysteroscopy?
- How Is the Hysteroscopy Procedure Done?
- What Types of Hysteroscopy Are There?
- What Are the Advantages of Hysteroscopy?
- Operative Hysteroscopy Procedures Aimed at Achieving Certain Goals
- Treatment of Congenital Pathologies of the Uterus
- Treatment of Hernia After Cesarean Section
- Treatment of Uterine Adhesions
- Removing the Displaced Intrauterine Device
- Are There Any Risks to the Hysteroscopy Procedure?
- When Should Hysteroscopy Be Performed?
A hysteroscopy is a procedure that aims to examine the inside of the uterus with a camera. Modern technologies allow us to examine many parts of our body and, if the situation requires it, perform surgical interventions.

Image-1: Hysteroscopy equipment.
Many endoscopic surgery options are available today. Some of them are the visual examination of the abdominal cavity (laparoscopy), joints, and the bladder (cystoscopy) with a camera.
How Is the Hysteroscopy Procedure Done?
Hysteroscopy is performed using a camera connected to a monitor. The procedure is performed without any incision by accessing the uterus through the vagina. If the procedure requires it, anesthesia can also be performed (as in surgical hysteroscopy). During diagnostic (office) hysteroscopy, anesthesia is not required since patients easily tolerate this procedure.
What Types of Hysteroscopy Are There?
Hysteroscopy, depending on the purpose of the procedure, can be divided into 2 groups:
- Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
- Operative Hysteroscopy
Diagnostic Hysteroscopy
Diagnostic hysteroscopy is performed to assess the inner part of the uterus using instruments with a diameter of approximately 4 mm, and telescopes with a diameter of 2 mm. This procedure does not require the expansion of the cervix or even the introduction of a gynecological mirror. Office hysteroscopy, as the name suggests, can be performed on an outpatient basis. The uterus is usually filled with a liquid or saline solution to obtain a clear image during an office hysteroscopy. Diagnostic hysteroscopy is usually performed to identify pathologies of the uterus. In the hysteroscope, in addition to the telescope channel, there is also a smaller channel. With the help of tools sent through it, you can open minimal adhesions in the uterus or remove displaced intrauterine spirals.
Operative Hysteroscopy
The basic equipment of this type is similar to office hysteroscopy. However, due to the use of a wider hysteroscope, this type of hysteroscopy allows for surgical interventions. This equipment with a diameter of approximately 10 mm can fit both a camera and surgical instruments. This type of hysteroscopy requires dilation of the cervix, as well as anesthesia, because this procedure can be painful. Again, to get a clear image, the uterus is usually filled with some liquid or saline solution.
What Are the Advantages of Hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is widely used in the world to identify problems of the uterus, as well as to assess its condition. Some of the possible applications of this procedure are listed below.
Uterine bleeding: Hysteroscopy is widely used in the diagnosis of the causes of deviations from the normal menstrual cycle, especially when this is accompanied by an increase in the time and number of bleeding. In patients with complaints of irregular bleeding, hysteroscopy allows both to recognize uterine pathologies (endometrial polyp, fibroids, cancer, etc.) and to remove fibroids or polyps. This procedure also allows for biopsies and tissue diagnostics in cases of cancer detection. In patients who have a thickening of the uterus, but there are no visible pathologies, an endometrial biopsy is analyzed to determine the cause.
Health assessment before IVF: Procedures of reproductive endocrinology and infertility treatment sometimes require a visual analysis of the state of the uterus before directly implanting fertilized eggs there. This is done by using diagnostic hysteroscopy.
Operative Hysteroscopy Procedures Aimed at Achieving Certain Goals
If there are previously known endometrial polyps or fibroids inside the uterus, they can be removed by operative hysteroscopy.
Treatment of Congenital Pathologies of the Uterus
With the help of operative hysteroscopy, the removal of the uterine septum, which is formed during its development, is also performed.
Treatment of Hernia After Cesarean Section
After a cesarean section, although rarely, a sac-shaped hernia may occur in the area of the suture location, which protrudes forward through the weakened area. With this treatment, surgical hysteroscopy is usually sufficient, but sometimes it may be necessary to use laparoscopy in parallel.
Treatment of Uterine Adhesions
Adhesions can occur in the uterus after such interventions as removal of fibroids, polyps, cesarean section, or curettage of the uterine cavity. In medicine, this condition is known as Ascherman’s syndrome. In this situation, the amount of menstrual bleeding either decreases or is completely absent. It also makes it difficult to conceive and can cause infertility. In cases of Ascherman’s syndrome, the adhesive process is stopped by performing a surgical hysteroscopy.
Removing the Displaced Intrauterine Device
An intrauterine device (a contraceptive device) can sometimes change its position in the uterus so that the threads of these devices is not observed. Shifting can sometimes cause problems such as a puncture of the uterus, bladder, intestines. The process of extracting intrauterine devices which filaments are not observed can be easily performed with the help of diagnostic hysteroscopy tools.
Are There Any Risks to the Hysteroscopy Procedure?
Although hysteroscopy, being a procedure performed without any incisions, may seem completely safe, in some cases, it is still associated with risk. Piercing of the uterus is one of the complications that occur when a hysteroscope is inserted into the uterus or during operative hysteroscopy. Some of the possible complications of hysteroscopy are bleeding, intoxication (when using a hyperosmolar solution to dilate the uterus), infections that may develop after the procedure, as well as intrauterine adhesions formed due to these infections. Since operative hysteroscopy uses anesthesia, this type of hysteroscopy may cause complications directly related to anesthesia (lung infection: pneumonia, problems due to insufficient ventilation (atelectasis), etc.).
When Should Hysteroscopy Be Performed?
The duration of the hysteroscopy depends on the purpose of the procedure. If a hysteroscopy is to be performed to assess the inside of the uterus, it is preferable to perform it in the first days of menstrual bleeding, when the inside of the uterus is not yet thickened. In cases of prolonged bleeding, when planning the procedure is not possible, depending on each case, it is carried out as soon as the right moment appears. Again, as a rule, special planning or calculations are not required for a hysteroscopy to treat uterine pathologies (for example, polyps, adhesions, fibroids).

