
Use of Medicines and their Effects During Pregnancy
September 14, 2023
What is Bladder Prolapse?
September 16, 2023
Use of Medicines and their Effects During Pregnancy
September 14, 2023
What is Bladder Prolapse?
September 16, 2023
What is Rectal Prolapse?
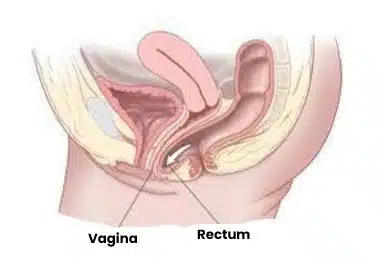
Figure 1: Rectal prolapse.
A section of the intestine also corresponds to the lower part of this opening. While the above-mentioned uterine functions can be performed thanks to the vaginal opening, a potential weak area is formed in the lower abdomen due to the same vaginal opening, and the uterus, bladder, or intestines can come down from this weak area and even go out of the body through the vagina. Here, the condition of displacement of the intestine, which should normally be located in the pelvic region in the abdomen, down the vagina and even hanging out of the vagina, is called rectal prolapse.
How does Rectal Prolapse Occur?
Both the small intestine and the large intestine can be pocketed, causing drooping out of the vagina. This occurs due to the relaxation of the pelvic floor. The most common causes of relaxation of the pelvic floor can be listed as follows: Normal birth (vaginal birth), episiotomy opening during normal birth, use of vacuum or forceps in difficult births, constipation, excessive straining on the toilet, age, cough, menopause, lifestyle, obesity, connective tissue diseases, systemic diseases such as diabetes, uterine and intestinal surgeries. With the increase in intra-abdominal pressure, the organs in the lower abdomen go down further and the muscles and ligaments here are faced with strain. All these situations destroy the supporting tissues in the pelvis.
What are the Symptoms of Rectal Prolapse?
Rectal prolapse can be mild or severe. Mild cases may not have any complaints. The most frequently mentioned complaints by the patients as the degree increases: change in defecation, not being able to empty when going to the toilet, the desire to go to the toilet frequently during the day, the need to support with hands while defecating, constipation, pain in the breech area, pain that can change with position during sexual intercourse, in the form of bleeding. Some symptoms vary according to the degree of bladder prolapse. All complaints can be evaluated by examination at the doctor's application.
How is Rectal Prolapse Diagnosed?
Rectal prolapse is diagnosed with a normal gynecological examination. Since the gynecological examination is performed in patients with the above complaints, visualization of the intestine that does not protrude from the vagina or that has protruded is sufficient for the diagnosis. In cases of early-stage rectal prolapse, if the mass protruding from the vagina cannot be seen during the gynecological examination, it may be necessary to examine it by pushing the patient on the table or by pushing after he/she stands up. In the patient who is standing up or straining, the rectum protruding from the vagina can be seen and the diagnosis of rectal prolapse can be made.

