
Urinary Incontinence in Women – Diagnosis and Treatment Methods
January 28, 2024
Pregnancy and Myoma – Risks, Follow-up and Treatment
January 28, 2024
Urinary Incontinence in Women – Diagnosis and Treatment Methods
January 28, 2024
Pregnancy and Myoma – Risks, Follow-up and Treatment
January 28, 2024
Uterine Prolapse - Diagnosis and Treatment Methods
The uterus is the reproductive organ that allows the fertilized human egg to settle and grow until birth. It is located in the lower part of the abdomen in an area called the pelvic region, which is surrounded by bone, muscle and connective tissue. Uterus is opened to the outside of the body by vagina that allows a passage of the lower part of our body in order for the menstrual bleeding to flow out, for the passage of sperm for pregnancy, and for the birth of the baby in case of pregnancy.
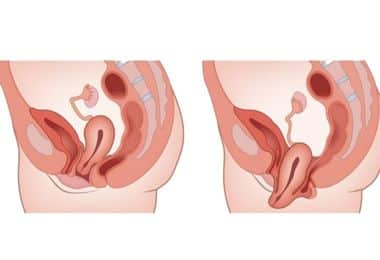
Image-1: Uterine prolapse
Thanks to the vaginal opening, the above-mentioned uterine functions can be performed, while a potential weak area is formed in the lower part of the abdomen due to the same vaginal opening, and the uterus, bladder or intestines can come down from this weak area and even come out of the body from the vagina. Here, uterine prolapse is the condition in which the uterus, normally be located in the pelvic region of the abdomen, is displaced downwards from the vagina and even sags outwards from the vagina.
Why Does Uterine Prolapse Occur?
Thanks to the ligaments that prevent the uterus from hanging down from the vagina, it is located in the anatomical region that should be normal. The ligaments of the uterus strongly grasp the uterus both on the sides and in the anterior-posterior plane in the area where it is located, preventing the uterus from descending downwards. In addition, the vagina, is surrounded by muscle and connective tissue, preventing both the vagina and the uterus from sagging downward. Weakness or damage of the ligaments of the uterus or the tissues around the vagina paves the way for uterine prolapse. In addition, continuous coughing and increasing internal pressure of the abdomen by constantly lifting heavy will also pave the way for sagging that will contribute negatively to this process. Uterine prolapse is more common in cases such as multiple births (vaginal birth), difficult birth and giving birth to large babies (vaginal birth), being overweight, smoking, advanced age, chronic constipation and straining.
What Are the Symptoms of Uterine Prolapse?
The most common complaints of patients with uterine prolapse are a feeling of fullness in the vagina, pressure, pain, and in advanced cases, a palpable or visible mass while lifting, straining or standing. There are symptoms that vary according to the degree of uterine prolapse. Those with mild sagging and those whose uterus does not come out of the vagina come with complaints such as constant pain and fullness, while those who have protruding from the vagina and have advanced uterine prolapse apply to the doctor with the complaint of a mass that is directly palpable. In some cases, the protruding uterus can be pushed upwards with the patient's effort, while in some cases, it is not possible to push the uterus to its former place. Therefore, the symptoms of uterine prolapse are not specific, while there is only pain and a feeling of fullness in the early stages, there are signs of a mass that is palpable or visible and comes out of the vagina in the advanced stages.
How Is Uterine Prolapse Diagnosed?
Uterine prolapse is quite easy to diagnose and is diagnosed by normal gynecological examination. Since gynecological examination is performed in patients with the above complaints, it is sufficient for diagnosis to see the uterus comes out of the vagina or that has come out. In cases of early uterine prolapse, if the mass protruding from the vagina cannot be seen during the gynecological examination, it may be necessary to re-examine the patient by straining on the table or by straining after standing up. Uterine prolapse can be diagnosed by seeing the uterus protruding from the vagina in the patient who is standing up or strained.
How Is Uterine Prolapse Treated?
Treatment in cases of uterine prolapse depends on many factors such as the age of the patient, fertility expectation, the degree of sagging, the patient's expectation from the treatment and her life expectation after the treatment, the experience of the physician, etc. If the degree of sagging is small and the uterus is at a level above the hymen in the vagina, and the complaints are minimal, pelvic floor exercises such as Kegel Exercises, which strengthen the pelvic floor to prevent the further progression of the prolapse, can prevent the problem from progressing further. In these exercises, the patient's compliance and moving away from the factors that cause sagging, if any, contribute positively to getting results. If the sagging is severe and the uterus is outside of the vagina, the surgical option is considered. Today, there are very effective surgical methods performed by both open and closed (laparoscopic) methods in the treatment of uterine prolapse, and if these operations are performed by experienced surgeons, the risk of complications will be less and lifelong permanent treatment can be achieved. In most cases, uterine prolapse surgeries performed with closed, that is, laparoscopic methods, most of the patients stay in the hospital for only one night, are discharged the next day and return to their daily lives within a few days. Since most of the patients see this problem as a problem that is encountered in the natural course of life and needs to be endured, and they do not report the problem with the idea of privacy, most patients do not seek treatment. However, knowing the existence of methods used in the treatment of uterine prolapse in today's modern medicine and providing lifelong permanent treatment will both contribute positively to the search for treatment and provide the opportunity for patients to get rid of this problem for life. Since it provides permanent treatment for a lifetime and the return to daily life after surgery is faster, we prefer suspension operations performed through the abdominal route, that is, through the abdomen and with the laparoscopic (closed) method in our clinical practice.

