
What Are Kegel Exercises?
May 15, 2023
Folic Acid Use in Pregnancy
May 28, 2023
What Are Kegel Exercises?
May 15, 2023
Folic Acid Use in Pregnancy
May 28, 2023
What Is Placenta Previa?
Placenta Previa is the name given to the condition where the placenta closes the cervix. As is known, the placenta is a vital organ for the fetus in the mother's womb, formed by some specialized cells from the fertilized egg, attached to the uterine wall and providing the nutrients and oxygen taken by the mother to the baby, and the metabolic wastes of the baby to be transferred to the mother's circulation.
The placenta, which should be formed and function in a healthy way throughout pregnancy, should be completely separated from the uterine wall and expelled within minutes after the birth of the baby. In normal pregnancies, the placenta is located mostly on the posterior wall of the uterus and less on the anterior, side walls or upper part of the uterus. Placentas that are located close to the cervix or that partially or completely cover the cervix are called "Plasenta Previa".
Placenta previa is seen in up to 5% to 30% of pregnancies (the frequency varies according to risk groups). As placenta previa poses a risk for some problems that may threaten the life of the mother and/or baby as explained below, placenta previa cases are defined as high-risk pregnancies and the conditions and accumulations sufficient for normal routine pregnancy and delivery may not be sufficient in placenta previa cases.
Why Does Placenta Previa Occur?
Risk factors for placenta previa are usually previous conditions of the uterus that are thought to cause damage to the inside of the uterus. Previous births, previous cesarean section operations (the risk increases with each cesarean section), previous curettages, smoking and cocaine use, chronic hypertension, multiple pregnancy, placenta previa are known as risk factors.
Are There Types of Placenta Previa?
Placenta previa is classified according to the relationship between the placenta and the inner opening of the cervix. If the placenta completely covers the cervix, "Plasenta Previa Totalis", that is, "Full Placenta Previa" is given. If the cervix covers the cervix partially, not completely, it is called "Plasenta Previa Subtotalis" or "Partial Placenta Previa". If the placenta reaches the cervix and does not close the cervix at all, it is called "Plasenta Previa Marginalis)".
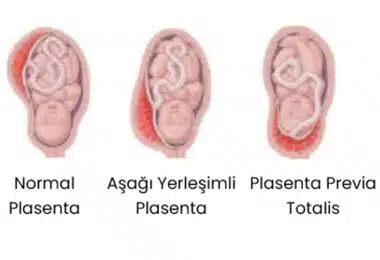
Image-1: Placenta previa and its types.
Even if the placenta does not reach the cervix and the widest distance between the cervix and the inner hole of the cervix is below 2 cm, it is called "Low Lying Placenta", in other words, "Lower Placenta". There are also suggestions for separating the two groups as those who have recently closed the inner hole of the cervix, and those who have not closed the inner hole, but extending here to 2 cm or less, and for the others (all placentas more than 2 cm from the cervix), there are suggestions for placenta with normal placement.
How Is Placenta Previa Diagnosed?
In addition to the clinical information of the patient, the diagnosis of placenta previa can usually be made with an accuracy of close to one hundred percent by ultrasonography. Most cases of placenta previa have bleeding complaints from the beginning of pregnancy. Bleeding is fresh red and unpredictable bleeding. In ultrasonographic evaluation, the relationship between the placenta and the cervix, that is, the inner hole of the cervix, can often be easily evaluated and diagnosed. In rare cases, ultrasonography may not be sufficient and magnetic resonance imaging may be required. In this way, the diagnosis of placenta previa is made. An important point to be considered here is the week of pregnancy.
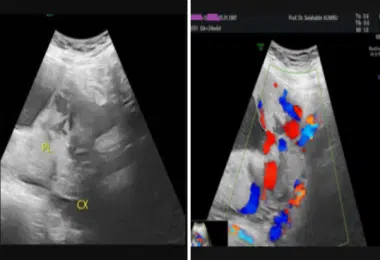
Image-2: Diagnosis of placenta previa on ultrasound.
Transvaginal ultrasonography (a) and doppler ultrasonography findings in the diagnosis area in a case of placenta previa with a diagnosis of placenta. (b) Passage of the placenta from the posterior wall of the uterus to the anterior wall and by completely closing the inner cervix in ultrasonography (a) and progression of the placenta deep into the uterine wall and even into the bladder/placenta accreta spectrum in color Doppler ultrasonography (b) PL: Placenta CX: Cervix.
In some of the pregnant women diagnosed with placenta previa in the first half of pregnancy, as the gestational week progresses and the uterus grows, the placenta will also go upwards. Therefore, some of the cases diagnosed as placenta previa at the beginning of pregnancy may cease to be placenta previa in the future. Therefore, it would be appropriate to be cautious while diagnosing placenta previa in the early stages of pregnancy and to give detailed information about the future process.
How Is Placenta Previa Treated?
In cases of placenta previa, management, gestational week, how noisy the picture of placenta previa is (blood loss, anemia, need for blood transfusion), the condition of the baby, and the type of placenta previa are related. The management of a placenta previa case that did not bleed during pregnancy, was only close to the cervix and did not close the birth canal, and a placenta previa totalis case that bled during pregnancy and required blood transfusion to the mother from time to time will be different.
In cases of placenta previa, the decision to deliver is made by considering many factors such as the type of previa, whether the picture is noisy with bleeding, the condition of the mother and the baby, the proximity/distance of the place where the patient lives to the full-fledged patient. Cesarean section surgery in placenta previa cases has different features and risks than cesarean section surgeries due to other reasons. Delivery of placenta previa cases should be done in centers where both an experienced team (perinatology, neonatology, urology specialists if reanimation is needed, etc.) and full-fledged hospital conditions (blood and blood products and necessary drugs can be easily found for the mother and baby, if needed, intensive care conditions are available).
Since preterm birth is more common in placenta previa cases, if the decision is made for premature birth and there is an opportunity, measures should be taken to prevent lung development on the one hand, cerebral palsy on the other hand, and to reduce the risk of damage to the neurological functions of the newborn baby. Bleeding should be expected more in placenta previa surgeries than in other ordinary cesarean sections. For this reason, on the one hand, blood preparation is done completely against possible bleeding, on the other hand, the most accurate decisions are made in the fastest way to minimize the blood lost during the operation, and to act quickly and carefully to minimize both the risk of loss of mothers and babies as well as injuries or undesirable consequences. will reduce.
The thing to keep in mind is that placenta previa itself is not lethal. Prenatal or postnatal bleeding accompanying placenta previa is fatal. The least bleeding, the fastest replacement of the lost blood, and the availability and accessibility of doctors with other expertise that may be needed will minimize the risks of both fatality and disability.

