
Proper and Regular Nutrition During Pregnancy
November 1, 2023
Pregnancy Process – Baby Development by Months
January 28, 2024
Proper and Regular Nutrition During Pregnancy
November 1, 2023
Pregnancy Process – Baby Development by Months
January 28, 2024
Ectopic Pregnancy - Causes and Treatment Methods
In a normal pregnancy, a fertilized egg (embryo) moves into the uterus through the fallopian tube and attaches to the lining of the uterus, where it continues to develop. In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg settles somewhere outside the main uterine cavity and continues to develop there. However, an embryo cannot live anywhere outside the uterus. If left unaddressed, an ectopic pregnancy can be fatal and pose a significant risk to the mother.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Tubal pregnancy is the most common type of ectopic pregnancy. This is a condition in which the embryo settles in the fallopian tube, moving towards the uterus.
A few other infections, especially sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, cause inflammation of the fallopian tubes. A fallopian tube that is damaged and deformed as a result of inflammation increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Almost all cases of ectopic pregnancy occur due to the implantation of an embryo in the fallopian tubes. In addition, it can rarely be localized in various areas, such as the cervix, ovary, or abdominal cavity.
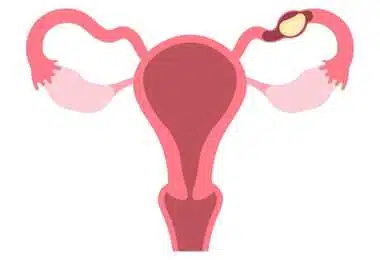
Image1: Ectopic pregnancy
Gestational age 35 years and older, previous ectopic pregnancies, and multiple curettes increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Hormonal imbalance may play a role in the occurrence of ectopic pregnancy. The hormone progesterone can slow down the movement of the fallopian tube, delaying its entry into the uterus through the fallopian tubes, which leads to an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy in the fallopian tubes.
Abnormal embryo development can also lead to an ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery to repair the fallopian tubes increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Contraceptive methods can also lead to ectopic pregnancies. The risk of developing an ectopic pregnancy is higher in the case of conception, despite the constant method of contraception, known as tubal ligation or colloquially “dressing.” Similarly, it increases the risk of conception despite the introduction of an intrauterine device (IUD).
Other reasons than those listed above.
- Chocolate cyst,
- Congenital or later developing disorders of the reproductive organs,
- Fertility-enhancing treatment.
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
In the early stages of pregnancy, a pregnant woman may not notice any signs of ectopic pregnancy. In some cases, there are also symptoms such as lack of menstruation, nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, and olfactory sensitivity, which are signs of the first period of pregnancy. However, as the embryo grows somewhere outside the uterus, the ectopic pregnancy condition will start to become more pronounced. An ectopic pregnancy that begins with vaginal bleeding and pelvic pain will be compounded by symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, persistent dizziness or fainting, low blood pressure, vomiting, weight loss, and shoulder pain. An embryo that continues to grow in the fallopian tube can cause the fallopian tube to rupture. This bleeding-causing condition requires immediate medical attention before it becomes life-threatening to the mother.
Risks That May Occur During An Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy causes the fallopian tube to rupture, which creates the risk of death due to internal bleeding if left untreated.
At the same time, an embryo growing in the fallopian tubes can also damage the fallopian tubes, resulting in loss of reproductive capacity.
Diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy
To prevent the occurrence of ectopic pregnancy, it is necessary to take several measures in advance. In a relationship, it would also be advisable to limit the number of partners and use sexual protection techniques to prevent sexually transmitted infections.
When planning a pregnancy, individuals who have one or more of the reasons listed in the name for ectopic pregnancy should maintain close contact with their doctor to minimize the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Ultrasound and blood tests are required to make a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy.
The presence of a gestational sac clearly located in the uterus can be determined by transvaginal ultrasound. It is also useful for diagnosing ectopic pregnancies through blood tests that determine the level of Beta HCG and progesterone.
Regular full blood tests and imaging techniques should be used to determine if there is a blood leak due to a ruptured fallopian tube if the doctor deems it necessary.
An ectopic pregnancy should be terminated after diagnosis. Places outside the uterus are not suitable for healthy embryo development.
If an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed at an early stage, you can use the method of treatment with medication. The drug, given in the form of injections, will stop the embryo's growth, which will lead to the termination of an ectopic pregnancy with an effect similar to a miscarriage.
If the medical treatment fails or an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed late, the ectopic pregnancy is interrupted by surgical intervention. During surgery, closed or open surgery will be performed depending on the condition of the fallopian tube, as well as on cases of bleeding and damage. In some cases, the fallopian tube can be saved while the damaged and torn fallopian tube is removed.
Blood tests will continue to be performed at regular intervals to determine that the procedures performed have shown the full effect.
Early detection of an ectopic pregnancy is important to eliminate the deadly risks that may occur in the expectant mother, as well as to minimize pregnancy complications that may occur later in life.
You can also read our other material, "What is ectopic pregnancy?".

